java.lang패키지
java 프로그램의 기본적인 클래스들을 포함하고 있는 패키지를 말한다.
-포함된 클래스나 인터페이스는 따로 import없이 사용 가능하다.
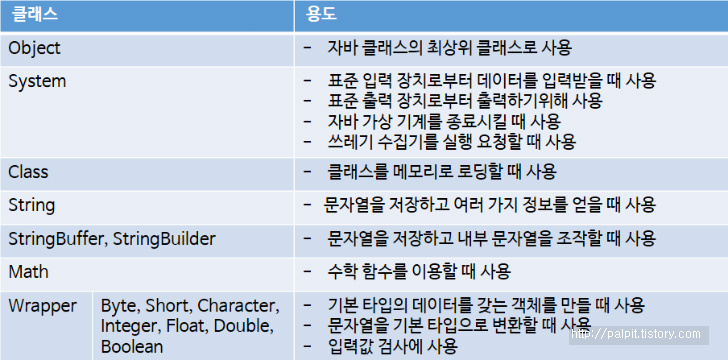
Object클래스
java의 최고 조상 클래스이다.
-일반적으로 다른 클래스를 상속을 명시적으로 하지 않는다면 상속한다.
11개의 메서드 존재
Object클래스의 메서드
객체의 주소 비교 메서드
객체의 논리적 동등이란?
-객체의 주소가 달라도 같은 값으로 보는 것
기본비교 예제
package kr.or.kihd.equals;
public class ObjectEqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Object클래스의 equals()
//주소 비교
Object object1 = new Object();
Object object2 = new Object();
//Object클래스의 equals()는 원론적으로 메머리번지 비교
boolean result1 = object1.equals(object2);
boolean result2 = (object1 == object2);
System.out.println("equals() : " + result1);
System.out.println("==연산자 : " + result2);
System.out.println(object1);
System.out.println(object2);
}
}
equals override 문자열,배열 추가 (논리적인 동등개념)
package kr.or.kihd.equals;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Student {
int age;
String name;
int[] subject;
public Student(int age, String name, int[] subject) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
System.out.println("오버라이징된 equals() 호출됨");
//타입변환 가능한지 여부를 알아보기 위해서 instanceof 연산자 이용
//Student가 obj의 객체이면
if(obj instanceof Student) {
Student student = (Student)obj; //Downcasting
//논리적 동등을 위해서 조건문을 설정
if((this.age == student.age)
&& (this.name.equals(student.name))
&& (Arrays.equals(this.subject, student.subject))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Arrays.equals 사용
package kr.or.kihd.equals;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student(10, "최지만");
Student student2 = new Student(10, "류현진");
System.out.println(student1.equals(student2));
Student student3 = new Student(10, "류현진");
Student student4 = new Student(10, "류현진");
System.out.println(student3.equals(student4));
}
}
객체의 문자정보를 알려주는 toString()
객체를 복제(clone())하는 메서드
-얕은복제 : 멤버변수 값만 복사함, 참조변수들은 번지를 서로 공유한다.
-깊은복제 오버라이딩 해서 사용 : 똑같은 객체로 만든다. (참조변수들의 번지 역시 서로 다르다.)
복제 예제
package kr.or.kihd.clone;
import java.util.Arrays;
//클래스의 복제가 가능하게 하려면, java.lang.Cloneable인터페이스를 구현해야한다.
public class Product implements Cloneable {
private String id;
private String name;
private int price;
private int[] arr;
private Apple apple; //클래스를 멤버로 정의
public Product(String id, String name, int price, int[] arr, Apple apple){
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.arr = arr;
this.apple = apple;
}
//getter
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public int[] getArr() {
return arr;
}
public Apple getApple() {
return this.apple;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "상품id : " + this.getId() +"\n" +
"상품이름 : " + this.getName() +"\n" +
"상품가격 : " + this.getPrice() +"\n" +
"배열값 : " + Arrays.toString(this.arr) +"\n" +
"Apple값 : " + this.apple.price;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {//깊은 복제가 되도록 재정의
//먼저 얕은 복제를 호출(기본형)
//Object 클래스의 clone()호출
Product cloned = (Product)super.clone(); //Downcasting
//참조타입들을 복제하는 코드
//배열타입 복제
cloned.arr = Arrays.copyOf(this.arr, this.arr.length);
//크기만큼 복제
//클래스 복제
cloned.apple = new Apple(this.apple.price);
return cloned;
}
public Product getProduct() {
Product cloned = null;
try {
//얕은 복제가 여기서 일어남(참조변수의 값들의 번지 공유)
cloned = (Product)this.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return cloned;
}
}
package kr.or.kihd.clone;
public class Apple {
int price;
public Apple(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
package kr.or.kihd.clone;
public class ProductTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product original = new Product("100", "TV", 300, new int[] {10,20}, new Apple(500));
//얕은 복제를 한 객체를 리턴
Product cloned = original.getProduct();
System.out.println(original);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(cloned);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
int[] arr1 = cloned.getArr();
; Apple apple = cloned.getApple();
int[] arr2 = original.getArr();
System.out.println("배열주소(복제객체) : "+arr1);
System.out.println("배열주소(원본객체) : "+arr2);
arr1[0] = 777;
apple.price = 1000;
System.out.println(original);
System.out.println();
System.out.println(cloned);
}
}




